This blog series presents links to new literature on topics of Medicinal and Organic Chemistry.
It is derived from surveys of the Table of Contents for the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters, Journal of Organic Chemistry, Journal of the American Chemical Society, Organic Letters, Organic Process Research and Development, Bioconjugate Chemistry, ACS Chemical Biology, Accounts of Chemical Research, Chemical Reviews ,and others with overviews provided by the blog author.
Novel Macrocyclic Antagonists of the CGRP Receptor Part 2: Stereochemical Inversion Induces an Unprecedented Binding Mode
Authors: Stacey M. Southall, Joydeep Banerjee, Jason Brown, Kristina Butkovic, Andrew D. Cansfield, Julie E. Cansfield, Miles S. Congreve, Gabriella Cseke, Francesca Deflorian, Martina Petrovic Hunjadi, Antun Hutinec, Trinadh Kumar Inturi, Renata Rupcic, Gordon Saxty, Stephen P. Watson
Abstract
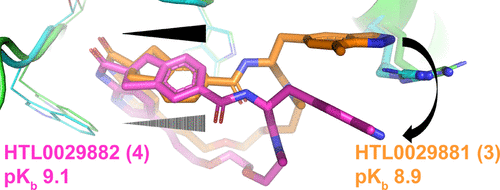
The diastereomeric macrocyclic calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) antagonists HTL0029881 (3) and HTL0029882 (4), in which the stereochemistry of a spiro center is reversed, surprisingly demonstrate comparable potency. X-ray crystallographic characterization demonstrates that 3 binds to the CGRP receptor in a precedented manner but that 4 binds in an unprecedented, unexpected, and radically different manner. The observation of this phenomenon is noteworthy and may open novel avenues for CGRP receptor antagonist design.
Overview
From the Watson group. CGRP antagonists are known drugs for migraine. Macrocycles are known CGRP antagonists. This paper describes structurally how two macrocyclo diastereomers bind the protein in different conformations with similar high potency. This could lead to a novel antagonist series in the future.
Nickel-Catalyzed Defluorophosphonylation of Aryl Fluorides
Authors: Zixi Zhu, Dale L. Boger
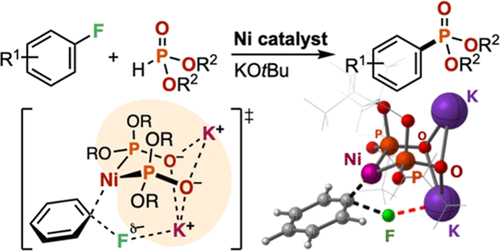
A Ni-catalyzed cross-coupling reaction between aryl fluorides and dialkyl phosphonates [HP(O)(OR)2] (R = secondary alkyl groups) in the presence of potassium tert-butoxide as a base is reported. The reaction converted various aryl fluorides into the corresponding aryl phosphonates even when electron-donating substituents were present on the aromatic ring. The combined experimental and computational studies suggested Ni–K+ cooperative action of a Ni(0) complex chelated with a strongly electron-donating ion-bridged dimeric phosphite ligand system [P(OR)2O–K+]2 that facilitates turnover-limiting C–F bond oxidative addition of aryl fluorides.
Overview
From the Higashida and Sawamura groups. There is already an established Pd-catalyzed cross-coupling of H-phosphonates with aryl-bromides or -iodides. This is a method for aryl-fluorides using Ni-catalysis. It is a useful expansion of the methodology.
Asymmetric Photochemical [2 + 2]-Cycloaddition of Acyclic Vinylpyridines through Ternary Complex Formation and an Uncontrolled Sensitization Mechanism
Authors: Zebediah C. Girvin, Laura F. Cotter, Hyung Yoon, Steven J. Chapman, James M. Mayer, Tehshik P. Yoon, Scott J. Miller
Abstract
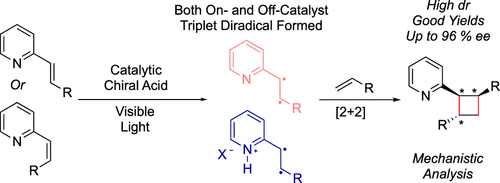
Stereochemical control of photochemical reactions that occur via triplet energy transfer remains a challenge. Suppressing off-catalyst stereorandom reactivity is difficult for highly reactive open-shell intermediates. Strategies for suppressing racemate-producing, off-catalyst pathways have long focused on formation of ground state, substrate-catalyst chiral complexes that are primed for triplet energy transfer via a photocatalyst in contrast to their off-catalyst counterparts. Herein, we describe a strategy where both a chiral catalyst-associated vinylpyridine and a nonassociated, free vinylpyridine substrate can be sensitized by an Ir(III) photocatalyst, yet high levels of diastereo- and enantioselectivity in a [2 + 2] photocycloaddition are achieved through a preferred, highly organized transition state. This mechanistic paradigm is distinct from,

Overview
From the Miller, Yoon and Mayer groups. Cyclobutanes can be expected to have a big impact on future medchem designs because they are still somewhat challenging to make on large scale. So, methodology is always developing. This paper shows how to control the asymmetry of the photo 2+2 cyclization of a styrene and an enamine to produce 1,2,3-trisubstituted cyclobutanes.
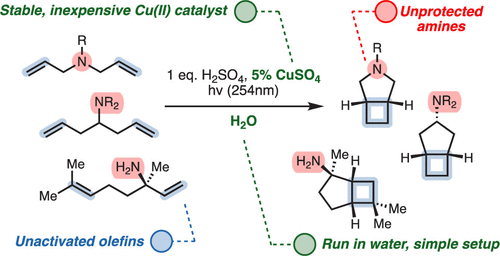
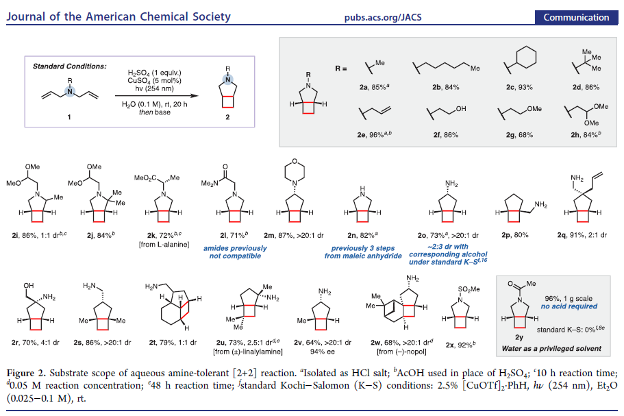
Aqueous Amine-Tolerant [2+2] Photocycloadditions of Unactivated Olefins
Authors: Carl M. F. Mansson, Noah Z. Burns
Abstract
The Kochi–Salomon reaction is the only photochemical [2+2] cycloaddition capable of combining two electronically unactivated olefins into a cyclobutane. Yet, the reaction has remained largely unexplored and suffers many drawbacks, most notably an intolerance to Lewis/Brønsted basic amines and amides. Since these groups are ubiquitous in biologically active pharmaceuticals, an amine-tolerant Kochi–Salomon reaction would greatly facilitate rapid exploration of novel drug scaffolds. Herein, we disclose a transformation that is run in water with the most widely available Cu(II) salts and mineral acids. Furthermore, we apply this methodology to synthesize a variety of amine-containing cyclobutanes, including known and novel pharmacological analogues.

Overview
From the Burns group. Continuing the cyclobutyl synthesis theme. This reaction works in water with CuSO4 and 254 nm light to produce cis-fused cyclobutyl-R5-amine ring systems.

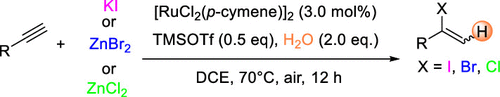
Ruthenium-Catalyzed Regioselective Hydrohalogenation of Alkynes Mediated by Trimethylsilyl Triflate
Authors: Yuye Bai, Zhenyuan Lin, Zhenying Ye, Dian Dong, Jing Wang, Lu Chen, Feng Xie, Yibiao Li, Pierre H. Dixneuf, Min Zhang
Abstract
Here we describe a ruthenium-catalyzed regioselective hydrohalogenation reaction of alkynes under mild conditions. Commercially simple halogen sources such as KI, ZnBr2, and ZnCl2 were employed to achieve this transformation. Alkynes derived from bioactive molecules such as l-(−)-borneol, l-menthol, and estrone were also suitable for the transformation, demonstrating the potential synthetic value of this new reaction in organic synthesis.

Overview
From the Chen and Zhang group. A way to convert a terminal alkyne into a 2-(Cl, Br or I)-substituted alkene. Most often these are aryl-alkynes but ethyl propiolate and a few other alkynes are in the example sets. The vinyl halides are useful moieties for a number of reasons.